How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation requires understanding various drone types, adhering to safety protocols, and developing skillful control techniques. This guide delves into each aspect, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies safely and effectively.
We’ll explore the nuances of different drone designs, from the nimble multirotor to the powerful fixed-wing, emphasizing pre-flight checks and safety procedures crucial for responsible operation. We’ll then move onto mastering the controls, progressing from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques like smooth filming and precise navigation. Finally, we’ll cover essential maintenance, legal compliance, and the basics of capturing stunning aerial footage.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective flight. This section details the operational differences between multirotor, fixed-wing, and single-rotor drones, providing pre-flight checks and a comparison of their advantages and disadvantages.
Multirotor, Fixed-Wing, and Single-Rotor Drone Operation
Multirotor drones, commonly known as quadcopters or hexacopters, utilize multiple rotors for vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) and maneuverability. Fixed-wing drones, resembling airplanes, require a runway for takeoff and landing and excel in long-distance flights. Single-rotor drones, or helicopters, offer VTOL capabilities and precise hovering, but are generally more complex to operate.
Pre-Flight Checks for Different Drone Types
- Multirotor: Check rotor blades for damage, ensure battery is securely connected and charged, calibrate the IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), and verify GPS signal strength.
- Fixed-Wing: Inspect the airframe for damage, check control surfaces for proper movement, ensure the battery is securely mounted and charged, and verify the propeller is properly attached and undamaged.
- Single-Rotor: Inspect the main rotor and tail rotor blades for damage, verify the swashplate is functioning correctly, check the battery and its connection, and ensure the tail rotor is properly functioning.
Comparison of Drone Types
| Feature | Multirotor | Fixed-Wing | Single-Rotor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Takeoff/Landing | Vertical (VTOL) | Runway Required | Vertical (VTOL) |
| Maneuverability | Excellent | Limited | Good |
| Flight Time | Moderate | Long | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to High | High |
Pre-Flight Procedures and Safety
Prioritizing safety is paramount before every drone flight. This section Artikels essential pre-flight procedures, emphasizing weather checks, airspace awareness, battery safety, and a comprehensive pre-flight checklist.
Safe Drone Launch Procedures
Before launching, check weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation), verify airspace authorization using a flight planning app (like AirMap or DJI Fly), and ensure there are no obstacles in the flight path. Always maintain visual line of sight with the drone.
Battery Safety and Charging
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow charging instructions carefully. Never leave batteries unattended while charging and store them in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Inspect batteries regularly for any signs of damage or swelling.
Pre-Flight Safety Checklist
- Inspect the drone for physical damage.
- Check the battery level and charge.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Confirm propeller security.
- Test all controls.
- Check weather conditions.
- Review airspace regulations.
Controlling the Drone: Basic Maneuvers
Understanding the drone controller is fundamental to safe and effective flight. This section explains the functions of control sticks and buttons and provides a step-by-step guide to basic maneuvers.
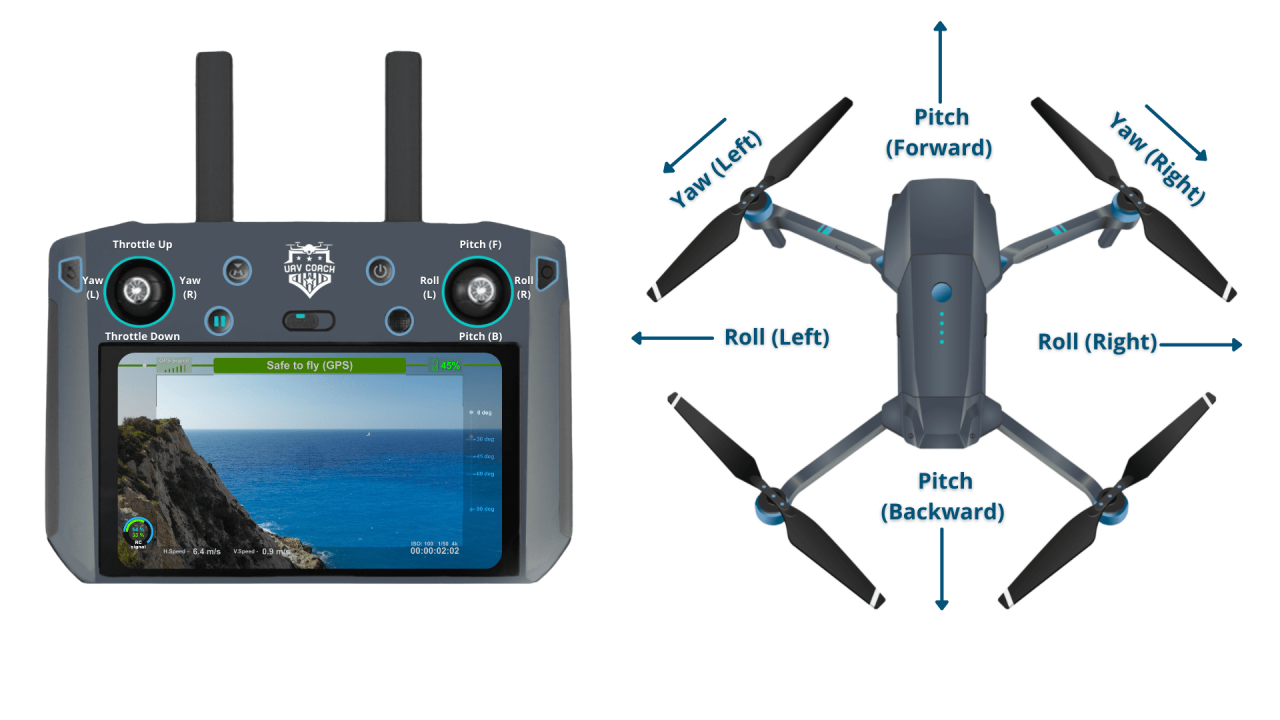
Drone Controller Functions
Most drone controllers feature two joysticks: the left joystick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls direction and throttle. Buttons on the controller typically manage functions such as camera control, return-to-home, and emergency stops.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
- Takeoff: Gently push the left joystick upwards.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady position by carefully adjusting the joysticks.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Push the right joystick forward or backward.
- Moving Left/Right: Push the right joystick left or right.
- Landing: Gently push the left joystick downwards.
Figure-Eight Maneuver
Imagine a figure-eight on the ground. The drone would start at the center, move upwards, then to the right in a semi-circle, down towards the bottom loop of the eight, then back to the center. It would then repeat this pattern in the other direction, completing the figure-eight shape.
Advanced Drone Operation Techniques
Mastering advanced techniques enhances drone control and expands creative possibilities. This section covers smooth and precise control, advanced maneuvers, and techniques for smooth subject filming.
Smooth and Precise Drone Control
Trim adjustments compensate for minor imbalances in the drone’s flight, ensuring stable hovering. Different flight modes (e.g., Attitude, GPS, Sport) offer varying levels of stability and responsiveness, allowing for precise control in different situations.
Advanced Maneuvers
Circling involves maintaining a constant radius around a point. Orbiting focuses on maintaining a constant distance from a subject while following its movement. Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously.
Smooth Subject Filming

To film a subject smoothly, maintain a consistent distance and altitude. Use the drone’s gimbal to adjust the camera angle and keep the subject centered in the frame. Practice smooth joystick movements to avoid jerky footage.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for prolonging drone lifespan and preventing accidents. This section addresses common malfunctions and details cleaning and maintenance procedures.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
- Low Battery: Charge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal or contact support.
Cleaning and Maintaining Drone Components, How to operate a drone
Clean propellers and the drone body with a soft cloth and mild detergent. Carefully clean sensors with a soft brush to avoid scratching. Inspect all components for wear and tear and replace parts as needed.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual inspection | Before each flight |
| Propeller cleaning | After each flight |
| Thorough cleaning | Monthly |
| Battery check | Weekly |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires adhering to local laws and regulations. This section emphasizes drone registration, airspace restrictions, and regional legal considerations.
Drone Registration and Permits
Many regions require drone registration before operation. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific requirements. Certain locations or activities might require additional permits.
Airspace Restrictions and Safe Flight Zones
Restricted airspace includes airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas. Always check airspace restrictions using a flight planning app before each flight. Maintain a safe distance from people and property during operation.
Learning to fly a drone involves understanding its controls and safety regulations. A crucial step is familiarizing yourself with pre-flight checks and procedures. For a comprehensive guide on the intricacies of piloting, you can consult this helpful resource on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Key Legal Aspects of Drone Operation
| Region | Registration | Airspace Restrictions | Other Regulations |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Example: USA) | FAA registration required | LAANC authorization for controlled airspace | Weight limits, visual line of sight |
| (Example: EU) | National registration requirements vary | Open categories and specific authorizations | Operator competency requirements |
Drone Photography and Videography Basics

Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography. This section covers framing, composition, stable shots, and various camera angles.
Framing and Composition
Utilize the rule of thirds for balanced composition. Consider leading lines and symmetry to create visually appealing images. Experiment with different perspectives to highlight the subject and its environment.
Achieving Stable Shots
Use the drone’s gimbal to minimize camera shake. Fly smoothly and avoid sudden movements. In windy conditions, adjust flight settings or choose a calmer location.
Camera Angles and Their Effects
High-angle shots provide a broad overview. Low-angle shots emphasize size and grandeur. Side angles offer dynamic perspectives. Experiment with different angles to achieve the desired effect.
Successfully operating a drone is a rewarding experience, blending technical skill with a keen awareness of safety and legal requirements. By understanding the different drone types, mastering control techniques, and prioritizing safe practices, you can unlock a world of creative and practical applications. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the journey, and enjoy the incredible perspectives that await you!
User Queries
What is the range of a typical drone?
Drone range varies significantly depending on the model and environmental factors. Typical ranges can be from a few hundred meters to several kilometers, but factors like signal interference and battery life will affect this.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life depends on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15-30 minutes of flight time per battery, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.
What happens if I lose signal to my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically guide the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone as much as possible.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of safety regulations and procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and troubleshooting, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will ensure you operate your drone safely and effectively.
Do I need insurance for my drone?
Drone insurance is highly recommended, especially for recreational use. It can protect you from liability in case of accidents or damage caused by your drone.
